Understanding Atherosclerosis: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Atherosclerosis is a serious condition where plaque accumulates in the arteries, making them narrow and stiff. This can result in CAD disease and other cardiovascular problems. Symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and dizziness can indicate signs of atherosclerosis. The disease can range from mild atherosclerosis to severe atherosclerosis. Early diagnosis and lifestyle changes, along with medications or surgical treatments, can help manage the condition and reduce the risk of complications. Managing atherosclerosis risk factors like high cholesterol, smoking, and poor diet is crucial to preventing or slowing the progression of the disease.
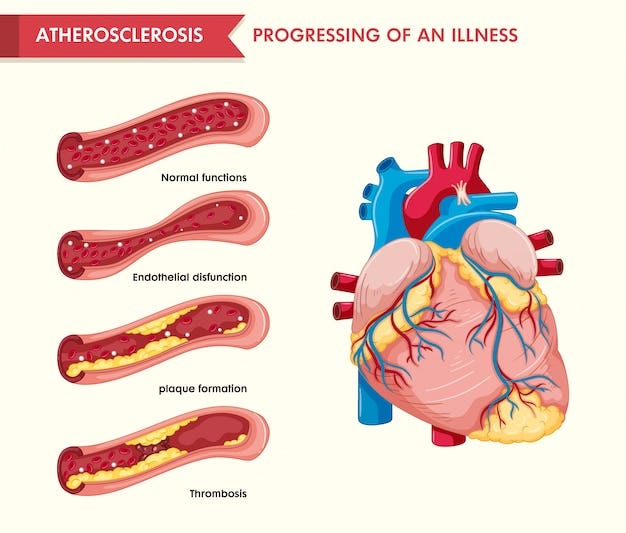
Atherosclerosis is a condition that affects the arteries in your body, making them narrower and harder. This happens when plaque builds up on the walls of your arteries, which are the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body. This buildup can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease. In this blog, we’ll talk about what causes atherosclerosis, the signs of clogged arteries, how it’s treated, and the risks involved.
What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is sometimes called “hardening of the arteries.” It is a type of atherosclerotic disease where plaque, made up of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, builds up inside the blood vessels. Over time, this plaque makes the arteries harder and narrower, which can cause blood flow to slow down or even stop.
This condition is often linked with CAD disease (Coronary Artery Disease), where the arteries that supply blood to the heart become blocked or narrowed, leading to heart attacks or other heart problems. Atherosclerosis of the aorta (the largest artery in the body) can also occur and can affect other organs by reducing the blood flow.
Causes of Atherosclerosis
Several factors can cause or contribute to atherosclerosis. These include:
- High cholesterol levels: Too much cholesterol in the blood can lead to plaque buildup.
- High blood pressure: When your blood pressure is too high, it can damage the walls of your arteries, making it easier for plaque to form.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar can damage blood vessels and lead to atherosclerosis.
- Inactivity: Lack of physical activity can increase the risk of high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and obesity, all of which contribute to atherosclerosis.
- Unhealthy diet: Eating too much fat, salt, and sugar can increase the chances of developing atherosclerosis.
Symptoms and Signs of Atherosclerosis
In the early stages of atherosclerosis, you may not notice any symptoms. But as the disease progresses, you may start to see signs of hardening of the arteries.
Here are some common signs of atherosclerosis:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina) — This happens when the heart doesn’t get enough oxygenated blood. It can feel like pressure or tightness in the chest.
- Shortness of breath — If the heart isn’t getting enough blood, it can lead to difficulty breathing.
- Fatigue — Feeling tired all the time, even after getting enough rest, could be a sign of CAD disease caused by atherosclerosis.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs or arms — If the arteries that supply blood to the arms or legs are clogged, you might feel weakness or numbness.
- Dizziness or fainting — Poor blood flow to the brain can cause dizziness or fainting.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor. These could be ascvd symptoms (Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease), which may require medical treatment.
Risk Factors for Atherosclerosis
Several things can increase your chances of developing atherosclerosis. These are called atherosclerosis risk factors. Some of these factors can be controlled, while others cannot.
- Age — As you get older, your risk of atherosclerosis increases.
- Family history — If heart disease runs in your family, you may be more likely to develop atherosclerosis.
- Gender — Men are generally at a higher risk of developing atherosclerosis at a younger age, but women’s risk increases after menopause.
- Unhealthy habits — Not exercising, smoking, and eating an unhealthy diet can all increase your risk.
- Health conditions — Having high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes increases the risk of atherosclerotic disease.
How is Atherosclerosis Diagnosed?
Doctors use several methods to check for signs of clogged arteries. These include:
- Blood tests — These tests can show if you have high cholesterol or high blood sugar.
- Physical exam — The doctor may check for weak pulses or listen to your heart for abnormal sounds.
- Imaging tests — Tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs can show if your arteries are narrowing or if there’s plaque buildup.
- Angiography — This test uses dye and special X-rays to see the inside of your arteries.
Types of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis can be mild or severe. The severity of the disease depends on how much plaque has built up in the arteries and how much it is affecting blood flow.
- Mild atherosclerosis — This is the early stage, where there’s some plaque buildup, but it doesn’t cause major problems yet.
- Severe atherosclerosis — This stage happens when plaque buildup is more advanced and blocks the blood flow, leading to serious health risks like heart attacks or strokes.
Treatment for Atherosclerosis
If you are diagnosed with atherosclerosis, your doctor may suggest several treatments. The goal is to reduce plaque buildup, improve blood flow, and prevent complications.
- Lifestyle changes — The first step is usually to make healthier choices, such as eating a better diet, exercising, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
- Medications — Doctors may prescribe medicines to lower cholesterol, control blood pressure, or help prevent blood clots.
- Heart calcification treatment — In cases where the arteries are severely calcified (hardened with calcium), treatments like angioplasty, stents, or surgery may be needed.
- Surgical options — In extreme cases, surgery may be required to clear blocked arteries or bypass them.
Preventing Atherosclerosis
While some risk factors cannot be changed, there are steps you can take to lower your chances of developing atherosclerosis:
- Eat a healthy diet — Focus on eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise regularly — Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
- Manage stress — Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation to reduce stress.
- Quit smoking — If you smoke, quitting will significantly lower your risk of developing heart disease.
- Monitor your health — Keep track of your blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels. Visit your doctor regularly.
A word from the Doctor —
Atherosclerosis is a serious condition that can affect many parts of the body, including the heart and brain. By understanding the causes, signs of atherosclerosis, and treatment options, you can take steps to prevent or manage the disease. If you have atherosclerosis risk factors, it’s important to make healthy changes to your lifestyle and work with your doctor to reduce your chances of complications.
Schedule a consultation with Dr. Sanul Corrielus right away if you have questions about your heart health!
.png)
Comments
Post a Comment